BlockChain Technology
Blockchain technology is a decentralized digital ledger system that records transactions across a network of computers. It ensures security, transparency, and immutability by grouping transactions into blocks, cryptographically linking them, and requiring consensus among network nodes before adding them to the chain. This technology finds applications beyond cryptocurrencies, including supply chain management, healthcare records, voting systems, and smart contracts.
What is BlockChain?
Blockchain can be defined as a chain of blocks that contains information. The technique is intended to timestamp digital documents so that it’s not possible to backdate them or temper them. The purpose of blockchain is to solve the double records problem without the need for a central server.
Blockchain can enhance the management and trading of ESGT by providing transparency, traceability, and efficiency. It enables transparent tracking of credits’ origins and ownership, streamlines transactions through smart contracts, and creates a global marketplace accessible to all. Blockchain also simplifies verification and compliance processes, incentivizing sustainable practices and contributing to climate change mitigation efforts.
How does Blockchain works?
Blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger system that records transactions across a network of computers. Transactions are verified, grouped into blocks, and added to the blockchain through a consensus mechanism. Once recorded, transactions are immutable and transparent. This process ensures security, integrity, and transparency in recording and verifying transactions without the need for intermediaries.
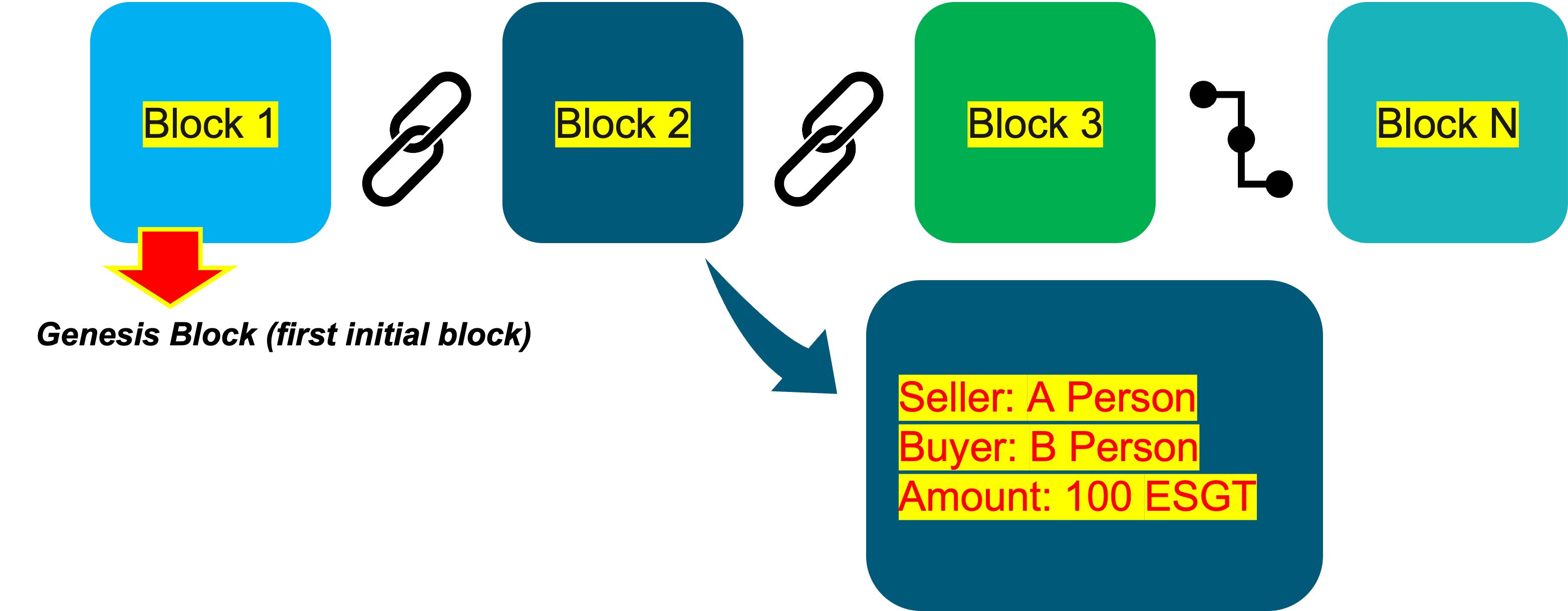
Chain Of Blocks That Contains Information
A Blockchain comprises interconnected blocks containing various types of information depending on the specific blockchain system in use.
Blockchain Security
Blockchain technology is considered highly secure due to its decentralized nature, cryptographic techniques, consensus mechanisms, immutability, and transparency. These features make it difficult for malicious actors to alter data or compromise the integrity of the network.
Blockchain Hash
Blockchain hashes are unique cryptographic identifiers assigned to each block in a blockchain. They are deterministic, ensuring consistency, and collision-resistant, minimizing the chance of two different inputs producing the same output. These hashes are crucial for maintaining data integrity, security, and immutability within blockchain networks.
TEAM















