What is a Carbon Credit?
Carbon Credit is a permit that allows the user to emit a certain amount of CO2e. It can be traded, sold, or retired.
1 Carbon Credit = 1 Tonne CO2e
How did Carbon Credit comes about?
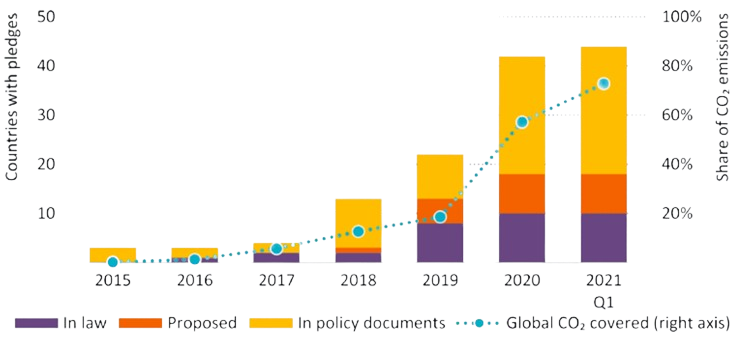
There has been a significant acceleration in net-zero emissions pledges announced by governments, with an increasing number enshrined in law
Notes: In law = a net zero pledge has been approved by parliament and is legally binding. Proposed = A net zero pledge has been proposed to parliament to be voted into law. In the policy document = a net zero pledge has been proposed but does not have a legally binding status
Paris Agreement
The Paris Agreement, established in 2015, aims to lead all countries toward significant reductions in worldwide greenhouse gas emissions, specifically carbon dioxide (CO2), with the ultimate target of achieving Net Zero emissions. This ambitious goal is intended to curb the long-term rise in average global temperatures to no more than 1.5°C. Currently, the agreement boasts participation from 194 entities, including 193 individual states along with the European Union.
Net Zero Pledges
Presently, approximately three-quarters of carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions stem from the energy sector. Globally, there is substantial commitment, with Net Zero pledges encompassing roughly 70% of CO2 emissions worldwide. To achieve Net Zero emissions by 2050, a reduction of 45% in emissions by 2030 is imperative.
The voluntary carbon market demand
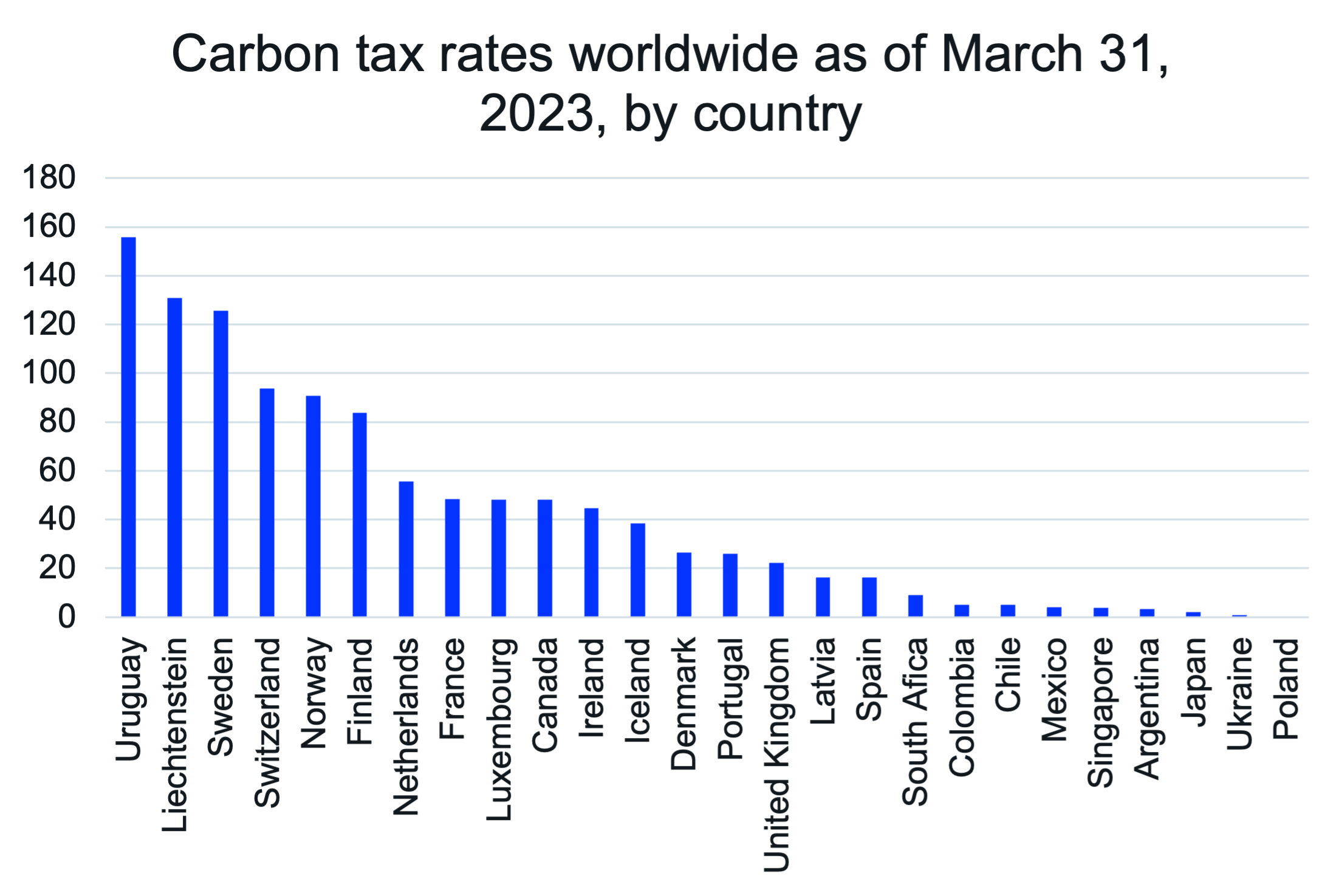
Global Carbon Tax
Uruguay had the highest carbon tax in 2023, at USD 155. The global average carbon tax in 2023 is USD 42.
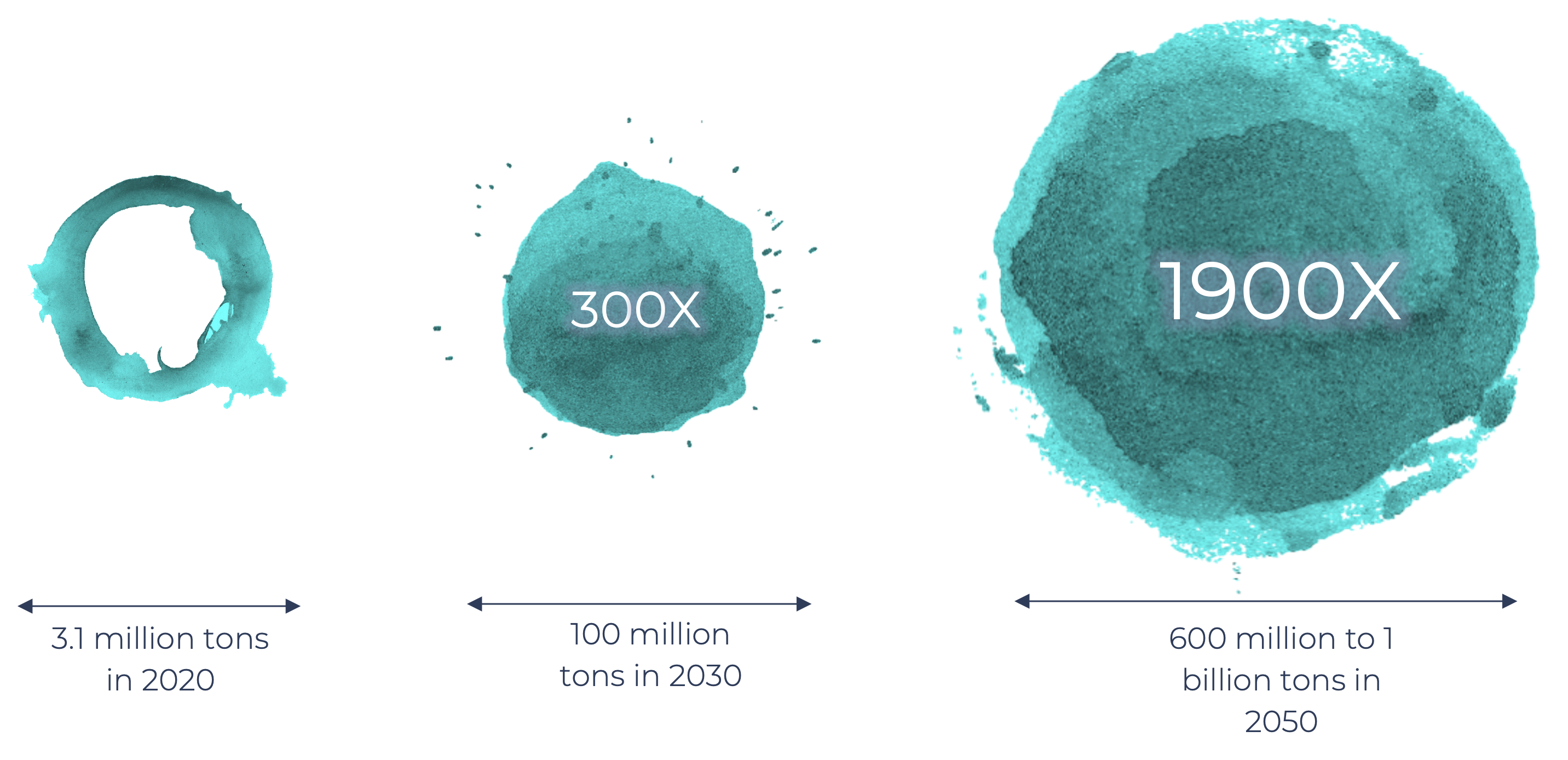
Projected Carbon Credit Floor Price
According to IMF chief Kristalina Georgieva stated that the real economy’s rate of change was still “far too slow” and that by 2030, the price of carbon must be at least $75 per tonne.
Potential Carbon Credits Market Size
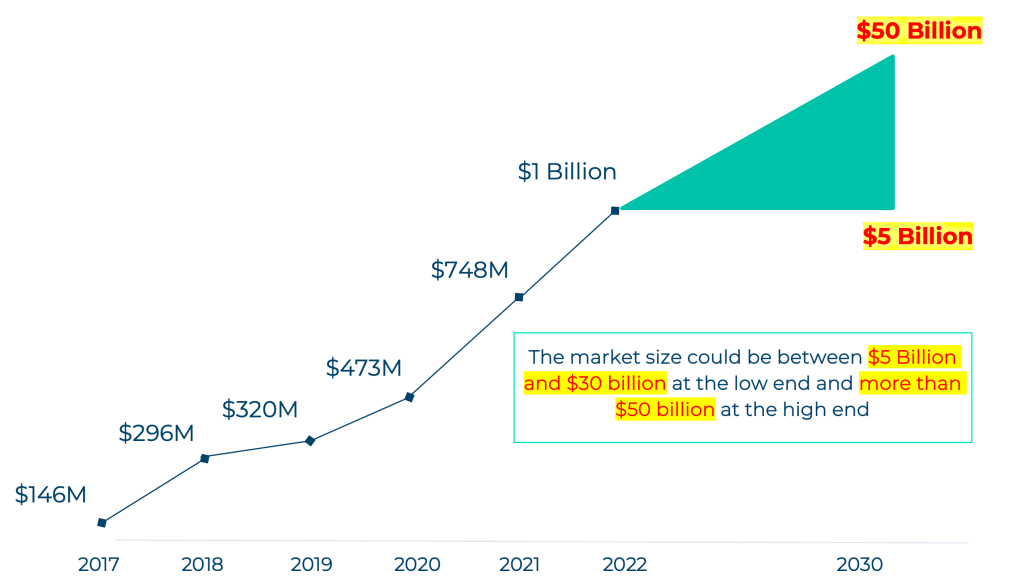
The focused carbon offset strategy has significantly boosted the value of voluntary offsets, surpassing $1 billion in 2022, marking a fivefold increase in under five years. McKinsey predicts a substantial growth in the Voluntary Carbon Market, potentially reaching $50 billion by 2030. Despite its promise, challenges lie ahead.
What affects the price of Carbon Credits?
The price of carbon credits, akin to any commodity, is shaped by supply and demand dynamics. High demand coupled with limited supply typically leads to price increases, whereas an oversupply tends to drive prices down.
Supply vs Demand
Several factors influence the supply and demand dynamics of carbon credits. Government regulations mandating emission reductions drive demand, while economic growth affects both emission levels and demand. Technological advancements in renewable energy and carbon capture influence both supply and demand, as does public perception of carbon markets. Additionally, the price of carbon credits itself affects both supply and demand, while international agreements and treaties set emission targets and trading frameworks. Natural events, such as extreme weather and changes in land use, can also impact emissions levels and the availability of carbon offset projects, further shaping supply and demand dynamics.

